Finding harmful content about yourself online is stressful enough. That stress often turns into frustration when the website hosting the content demands payment to remove it.
This is known as exploitative removal practices.
These practices occur when a website publishes damaging, personal, or misleading content and then charges a fee to take it down. In many cases, the content is designed to pressure individuals to pay rather than to offer a legitimate correction or dispute process.
The good news is that you are not powerless. There are clear, documented ways to report exploitative removal practices and limit their impact, even if the content itself remains online.
This guide explains how reporting works, where to report, and when to escalate the issue.
Key Takeaways
- Exploitative removal practices involve charging money to remove harmful or personal content.
- Search engines may remove results tied to exploitative practices even if the content stays live.
- Website owners and hosting providers can be contacted directly in many cases.
- Certain types of content qualify for legal, regulatory, or law enforcement reporting.
- Structured reporting often works better than confrontation or payment
What Are Exploitative Removal Practices?
Exploitative removal practices refer to situations where a website:
Publishes personal or damaging information
Creates pressure by ranking content prominently
Offers removal only after payment
Provides no legitimate dispute or correction process
These sites often rely on fear, urgency, or embarrassment to generate revenue. While not always illegal, these practices violate the policies of major search engines and many hosting providers.
Understanding this distinction is important. You may not be able to force the site to delete the content immediately, but you can often reduce its visibility and disrupt the incentive structure behind it.
Here is an example of a “company” that uses exploitative removal practices on its own website.
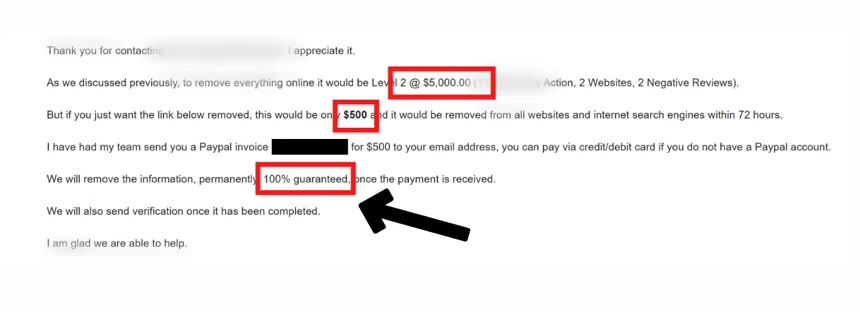
If you are in a situation where you need this information hidden immediately, you may be tempted to pay the ransom.
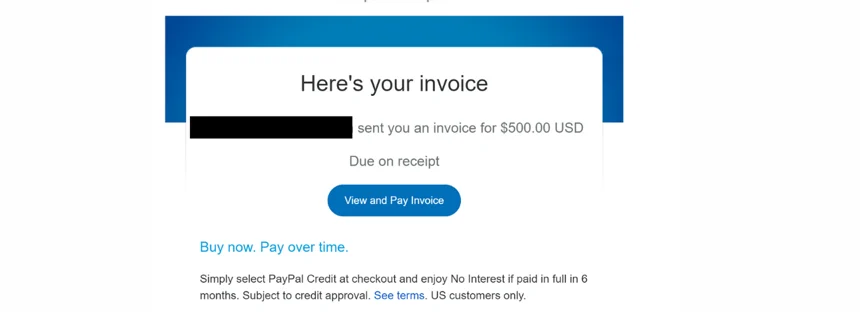
However, you must understand that the company will only republish it on another website and request additional funds. NEVER pay a ransom.
The Guaranteed Removals Myth
You should be skeptical of any company that guarantees removal from a particular website. If the company provides “guaranteed removals,” they are usually the owners or partners of the website.

A reputation management strategy that focuses solely on content removal leaves you open to 2 problems:
- The content being republished
- New negative content in the future
Content removal is an important part of your reputation management strategy, but it should not be the only strategy. You must provide new content to replace it.
Google is a data aggregate. They grab any relevant content they find that mentions your name, and if there is no new content, they will only display the negative.
Why Reporting Matters
Many people feel stuck and assume paying is the only option. In reality, payment often reinforces the behavior and may even lead to reposting or future demands.
Reporting exploitative removal practices serves two purposes.
First, it can result in search engines removing the content from search results, which significantly reduces exposure.
Second, it creates a record that can support further action if the behavior continues.
Reporting Exploitative Removal Practices to Search Engines
Search engines do not control what websites publish, but they do control what appears in search results.
When a site engages in exploitative removal practices, search engines may take action against the site itself.
Reporting to Google Search
Google has a specific reporting process for websites that charge for content removal.
If you encounter a site that demands payment to remove harmful content, you can submit a report explaining the situation. Google may remove the page from search results even if the website refuses to take it down.
This is often one of the most effective steps, as search visibility is what gives these sites leverage.
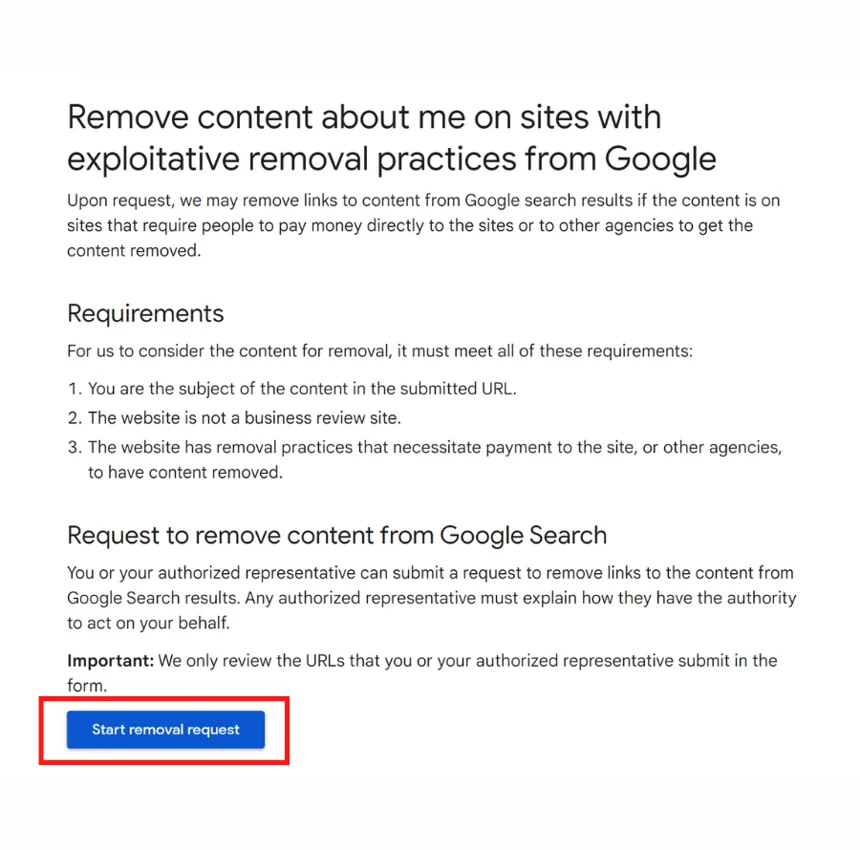
You must be the subject of the content or explain your relationship to the person described in the content.
Reporting to Other Search Engines
Other major search engines maintain similar policies against abusive or exploitative behavior. While processes vary, reports typically require:
The URL of the content
A description of the removal demand
Evidence that payment was requested
Removing a page from search results does not erase the content, but it dramatically reduces its impact.
Contacting the Website or Hosting Provider
In some cases, the most direct approach is still worth attempting, especially before escalating.
Contacting the Website Owner
Look for contact information on the website itself. This may include an email address, contact form, or legal notice.
When reaching out:
Clearly identify the specific URL
State why the content is harmful or inaccurate
Avoid emotional or threatening language
Keep the message factual and professional
While exploitative sites often ignore requests, some do respond when they realize the issue is being documented.
Contacting the Hosting Provider
If the website owner does not respond or is anonymous, the next step is the hosting provider.
Most hosting companies prohibit abusive, deceptive, or extortion-like behavior under their terms of service. Reporting the site to its host can sometimes lead to warnings, suspension, or content review.
To do this, you will need:
The website URL
A description of the exploitative removal demand
Any supporting evidence
Hosting providers are not obligated to act, but many will investigate clear policy violations.
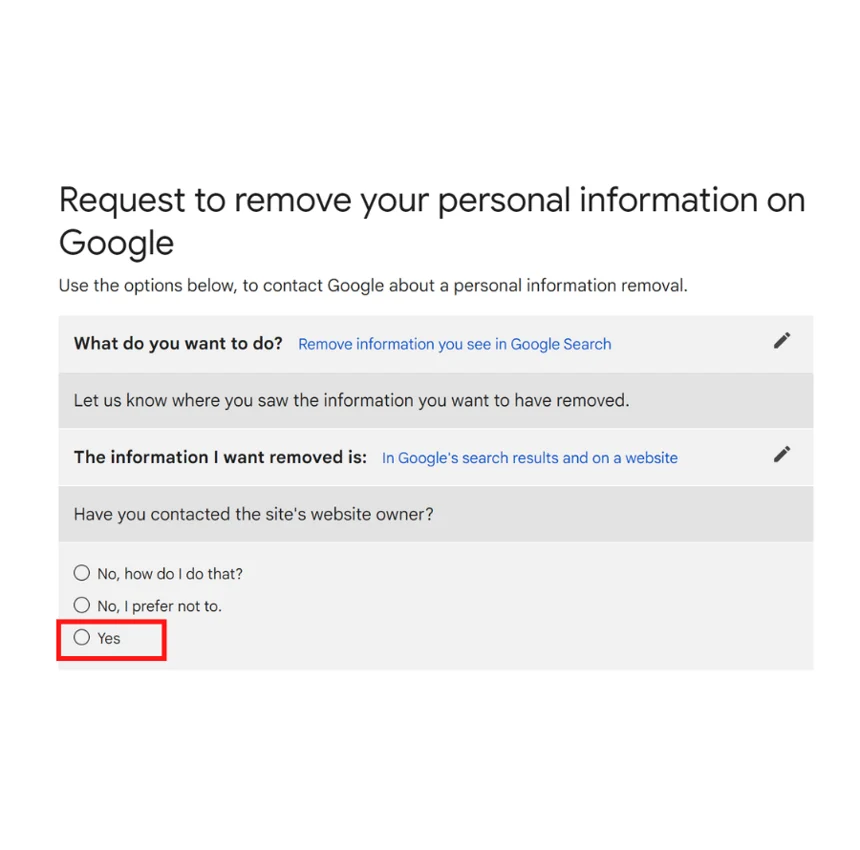
Note: You must contact the website owner before filing a removal request for exploitative removal practices. Select “yes”
Legal and Law Enforcement Reporting Options
Some forms of content go beyond exploitative practices and enter clearly illegal territory. In those cases, stronger options are available.
Non-consensual explicit content or Doxxing
If the content includes intimate images shared without consent or exposes sensitive personal information, you may be able to use specialized reporting tools.
Search engines provide dedicated forms for reporting non-consensual explicit images and doxxing-related content. These requests are often prioritized due to the harm involved.
For young people, the Internet Watch Foundation offers reporting tools designed specifically for rapid response.
Copyright Infringement and DMCA Takedowns
If the content uses material you own, such as photographs you took or original written content, copyright law may apply.
In these cases, you can submit a formal DMCA takedown notice to:
The website
The hosting provider
Search engines display the content
Copyright-based removals are often effective because they rely on established legal frameworks rather than discretion.
Law Enforcement Reporting
When content involves threats, severe harassment, fraud, or child exploitation, law enforcement should be contacted.
In the United States:
Online crimes can be reported to the Internet Crime Complaint Center, operated by the FBI
Crimes involving children should be reported to the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children
Law enforcement involvement is appropriate when safety or criminal behavior is involved, not just when reputation concerns are raised.
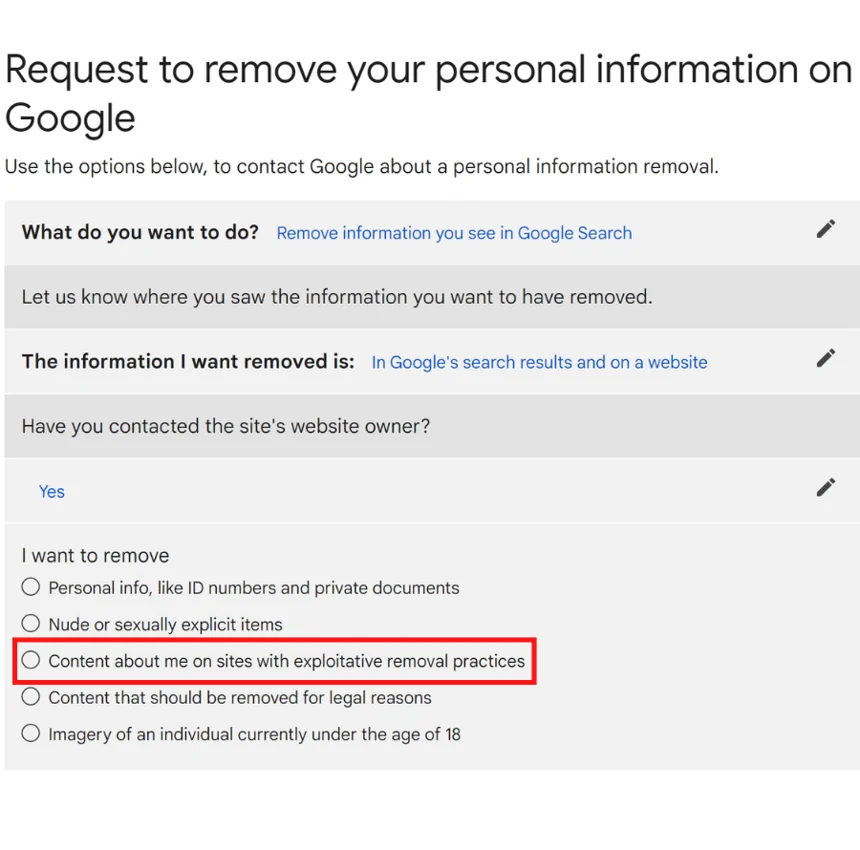
You can select the type of content you want to file a removal for.
Here are the options:
- Personal info, like ID numbers and private documents
- Nude or sexually explicit items
- Content about me on sites with exploitative removal practices
- Content that should be removed for legal reasons
- The imagery of an individual currently under the age of 18
Select “Content about me on sites with exploitative removal practices”.
Have you determined that the website(s) you are reporting here have exploitative removal practices?
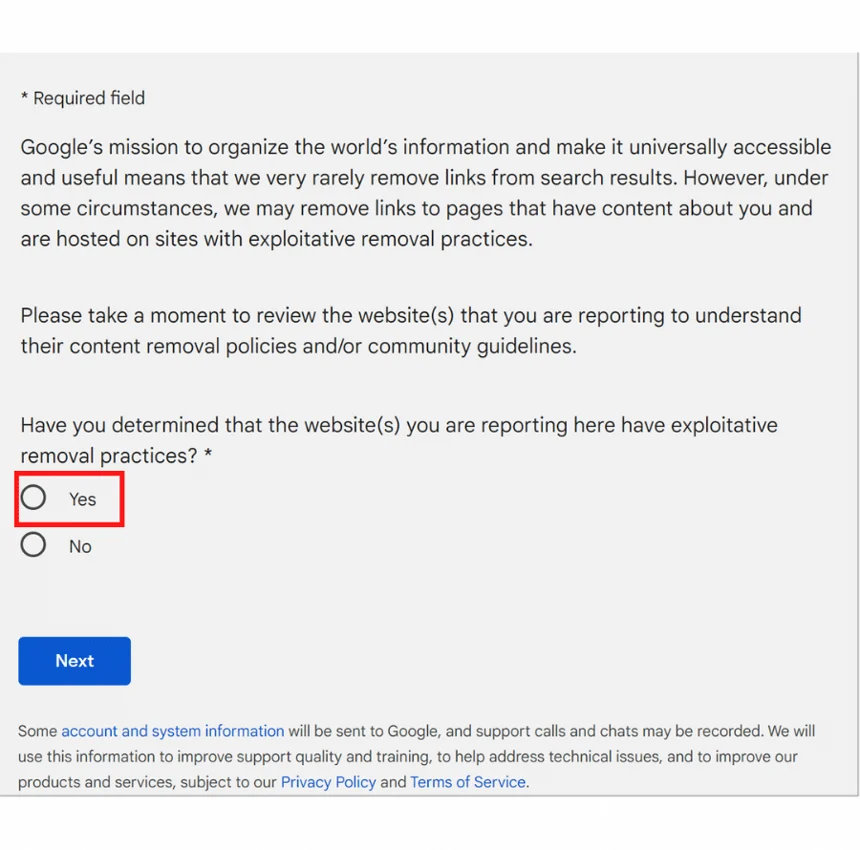
At this point, you are verifying that you have evidence of exploitative removal practices. Select “Yes”.
Fill out your personal information.
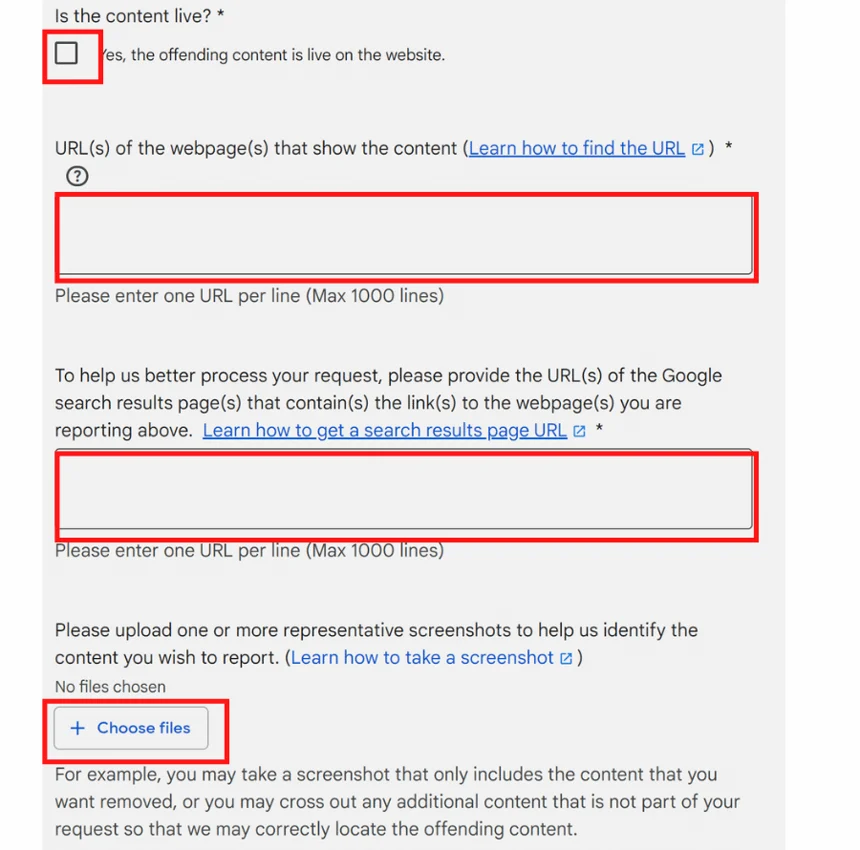
Complete the form to the best of your ability. Once you get to the section to upload a screenshot, upload your proof of exploitative removal practices.
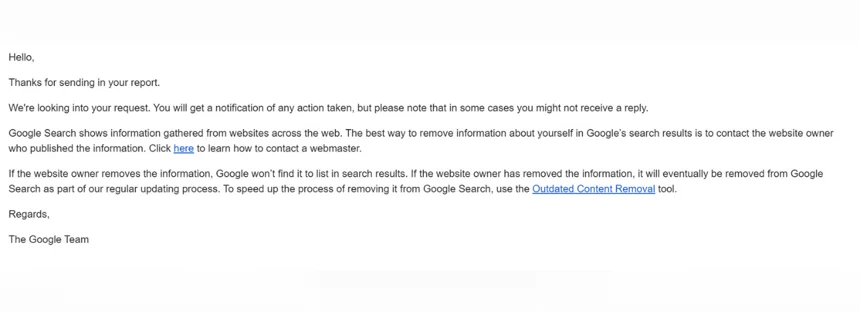
Once you submit the form, you will receive a notification that Google is investigating your request.
Consulting Professionals When the Situation Escalates
Some situations require additional support, particularly when content persists across multiple sites or platforms.
Legal Counsel
An attorney can advise on options such as cease-and-desist letters, subpoenas, or court orders. In some cases, legal action can compel removal or create leverage that informal requests cannot.
Reputation and Privacy Professionals
Professionals who specialize in online reputation and privacy can help coordinate reporting, documentation, and visibility reduction. While these services typically involve fees, they focus on lawful removal pathways and long-term risk reduction rather than quick fixes.
Practical Steps to Take Before Paying Anything
If you encounter exploitative removal practices, pause before responding.
Consider these steps first:
- Document all communication and demands
- Report the site to search engines
- Attempt contact through official channels
- Check whether the content qualifies for policy or legal removal
- Evaluate whether reducing visibility is sufficient
In many cases, removing the incentive is more effective than negotiating with the source.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are exploitative removal practices?
They occur when websites demand payment to remove harmful or personal content, often without offering legitimate dispute processes.
Can Google remove content from the internet?
No. Google can remove pages from search results, which limits visibility, but it does not control the original website.
Should I pay a site to remove content?
Payment often reinforces the behavior and may not guarantee permanent removal. Reporting and documentation are usually safer first steps.
What if the content is true but harmful?
Even true information may violate platform policies or privacy standards, especially when used coercively. Reporting is still appropriate.
When should I involve law enforcement?
If the content includes threats, criminal harassment, fraud, or child exploitation, law enforcement should be contacted immediately.
Conclusion
Exploitative removal practices thrive on fear and urgency. They rely on the assumption that individuals feel they have no options.
That assumption is wrong.
While you may not always be able to force immediate deletion, you can report abusive behavior, reduce visibility, and escalate appropriately. Search engines, hosting providers, and legal frameworks all play a role in limiting these practices.
The most important step is not to act out of panic.
Document the situation.
Use the reporting tools available.
And choose responses that protect your long-term reputation rather than rewarding exploitation.
Control comes from strategy, not payment.

West Virginia alumni with a background in marketing and sales for both established companies and startups.

