Most people know Bing as Microsoft’s search engine. It’s the box that pops up in Edge or the one that powers your Windows search bar. But few people know how it really works.
In this article, you’ll learn what happens behind the scenes every time you type something into Bing. You’ll see how it crawls the web, how it ranks pages, how it integrates artificial intelligence, and what makes it different from Google.
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how Bing’s search engine works and a few ways to use that knowledge to your advantage.
Bing Search Engine Fundamentals
Bing is Microsoft’s main web search engine. It’s designed to index, analyze, and rank billions of web pages to answer queries across text, images, video, news, and maps.
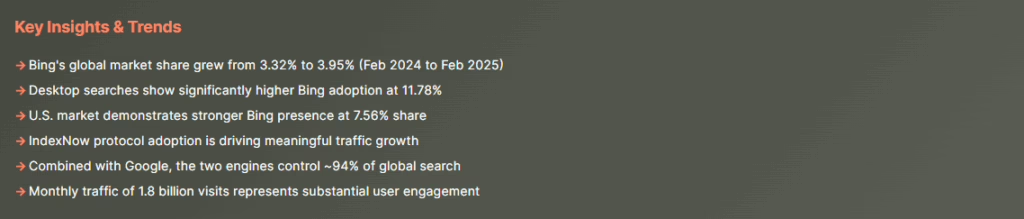
What makes Bing interesting is its connection to Microsoft’s larger ecosystem. It powers results for Windows, Edge, Cortana, and even voice assistants on smart devices. Bing is more than a website. It’s the engine behind how Microsoft users access information.
From a technical view, Bing uses distributed data systems that store and retrieve massive amounts of information in milliseconds. Its design focuses on three things: speed, accuracy, and quality. The system constantly refines results based on user behavior and feedback.
But understanding Bing starts with how it discovers content.
Search Integrity and Controls
Before any result shows up, Bing checks for trust and safety.
The first layer is content control. Bing filters harmful or explicit material using SafeSearch and similar filters. It enforces strict policies on malware, scams, or spammy sites to make sure users aren’t misled.
Next is duplication. The web is full of repeated pages, and Bing tries to choose one “canonical” version to avoid showing copies. It respects canonical tags and meta directives like “noindex” to manage duplicates.
There’s also human oversight. Bing employs review teams that manually check suspicious sites and enforce penalties when needed.
Finally, Bing applies a set of real-time quality checks before showing results. These steps look for spam, outdated links, and weak sources. By the time you see the search page, the engine has filtered and ranked hundreds of possible results behind the scenes.
User Experience and Interface
The next layer is how users actually interact with Bing.
Bing’s interface focuses on clarity. The homepage is minimal with a single search bar and background image. Once you type a query, results appear with bolded keywords and clean snippets that summarize the content.
The goal is to help users scan results quickly. Titles are straightforward. Snippets show exactly where the keywords appear.
Bing also uses structured data to make results more visual. You might see star ratings, images, prices, or FAQs pulled from page markup. These features help users find what they need without clicking multiple results.
Another part of the user experience is personalization. Bing remembers previous searches, location, and language to tailor results. If you search for restaurants, it prioritizes nearby ones. If you often search tech terms, Bing starts surfacing tech news.
It’s designed to anticipate your needs, not just react to what you type.
Indexing and Crawling Processes
Everything starts with crawling.
Bingbot is Bing’s main crawler. It travels across the web, following links, reading content, and discovering new pages. It obeys robots.txt files and crawl-delay instructions from websites to avoid overloading servers.
But Bing doesn’t just crawl randomly. It uses scheduling. Sites that change often are crawled more frequently. Pages that rarely update are checked less.
Modern sites rely heavily on JavaScript, so Bing uses a rendering engine to process these pages like a browser would. This lets it see dynamic content that older crawlers might miss.
Bing also uses something called IndexNow. It’s a system where websites can notify Bing directly when a page is added, updated, or deleted. Instead of waiting for the crawler to find the change, Bing can re-index it right away. This makes the search index fresher and more efficient.
After crawling, Bing parses the content. It reads the HTML, extracts headings, text, links, and metadata, and filters out anything marked as “noindex.” It calculates signals like keyword frequency, link context, freshness, and user engagement potential.
When pages are processed, Bing stores them in a massive index. The index is split into shards across servers to allow quick retrieval. It’s constantly updated as new content comes in and old data gets replaced. The process happens at scale every minute of every day.
Search Algorithms and Ranking Factors
Once a user enters a query, Bing begins ranking.
The process starts with understanding intent. Bing analyzes the query to determine what the user is trying to find. It identifies whether it’s a question, a purchase intent, or a request for local information. It then expands or refines the query if needed.
Bing retrieves a set of candidate pages that match the terms. These pages are scored across hundreds of signals.
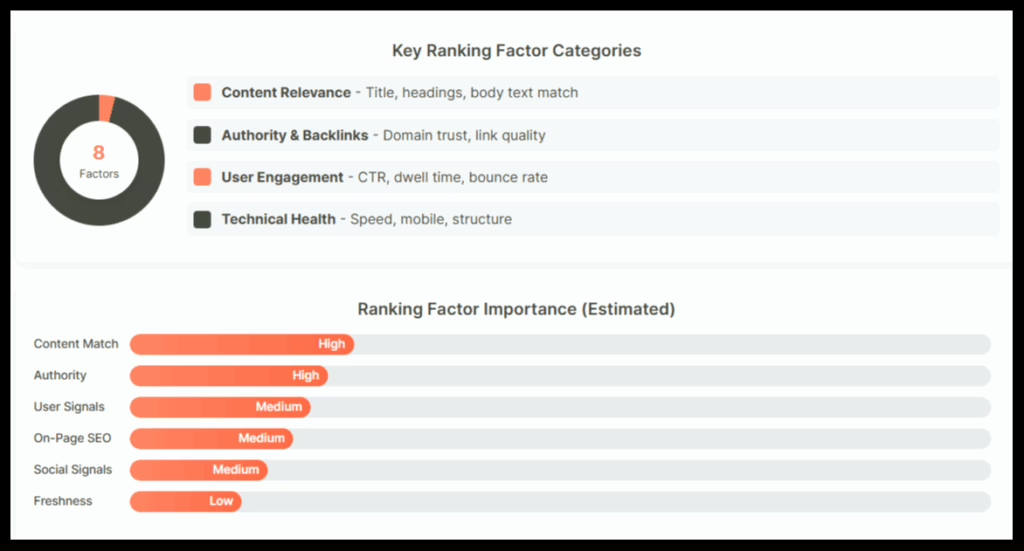
Relevance comes first. Bing looks for exact matches in the title, URL, and body. It also considers synonyms and context.
Authority comes next. Pages with quality backlinks from trusted sites tend to rank higher. Bing often values links from educational or government domains more heavily.
Freshness matters too. For trending topics or breaking news, Bing prioritizes newer content.
User behavior plays a major role. Pages that get higher click-through rates or longer visit times are rewarded because they indicate satisfaction.
Technical factors are also important. Fast loading, mobile responsiveness, and clean site structure improve a page’s performance in Bing rankings.
One notable difference from Google is how Bing uses social signals. Likes, shares, and engagement from social media can influence rankings. While it’s not a direct ranking factor everywhere, Bing treats social proof as a sign of content credibility.
All these factors combine into a machine learning model that determines the final order of search results.
SEO and Optimization for Bing
If you’re optimizing a site for Bing, there are specific steps that help more than generic SEO tactics.
Start with clarity. Bing prefers exact keyword matches. Use your target phrases in the title tag, heading, URL, and early in your content.
Structure matters. Keep your navigation simple, your URLs descriptive, and your internal links logical.
Add structured data. Use schema markup for products, FAQs, events, and articles. Bing uses this to enhance how your pages appear in results.
Avoid heavy JavaScript pages that hide content from crawlers. If your site uses JavaScript frameworks, use server-side rendering or pre-rendering so Bing can read the content properly.
Keep your content updated. Bing rewards freshness, especially for topics that evolve quickly.
Focus on content quality. Write detailed, clear, and accurate information that matches user intent.
Make sure your site loads quickly and works well on mobile devices.
Build links naturally. Bing values backlinks, but it prioritizes quality over quantity. Links from relevant and reputable sites carry more weight than random mentions.
Don’t ignore social activity. Bing’s algorithm pays attention to how your content performs on platforms like Facebook, X, and LinkedIn.
Use Bing Webmaster Tools. It’s free and provides insights into crawl errors, keyword performance, and indexing. You can submit sitemaps, request indexing, and see how Bing views your pages.
Activate IndexNow. It ensures your updates are indexed fast, without waiting for Bingbot.
For content strategy, target long-tail searches. Bing users often type full questions or longer phrases. Niche queries can drive consistent traffic.
If your audience is local, register your business in Bing Places to appear in map results and local packs.
When you combine these steps, you create a site that Bing can easily crawl, understand, and trust.
Artificial Intelligence and Generative Features
Bing has changed a lot in the last few years with the integration of artificial intelligence.
Its AI features don’t replace the search engine. They enhance it.
When users ask a question, Bing can generate summaries that pull from multiple trusted sources. This saves time for quick answers.
It also powers a conversational mode known as Bing Chat. In this mode, users can continue asking questions in natural language, and Bing refines its answers using context from previous queries.
The AI layer makes it easier for Bing to understand what you want. It knows when you’re looking for information, comparisons, or ideas. It fixes spelling mistakes, adds to searches, and even rewrites them to get better results.
AI also helps with features like “related questions” and “next steps,” which let consumers dig further.
For site owners, this means your content must still exist in the traditional index. Bing’s AI features pull from that base. High-quality, factual, and clearly structured content has the best chance of being summarized or quoted in these AI-powered results.
Specialized Bing Services and Features
Beyond search, Bing powers a collection of specialized tools and vertical engines.
Image Search lets users explore photos, illustrations, and product images. It uses object recognition and metadata to deliver results.
Video Search provides previews and filters for duration, resolution, and source.
News Search is updated in real time and focuses on trusted publishers. Bing integrates regional and global news outlets to tailor coverage to each user’s location.
Maps and Local Search power results for directions, business listings, and local events. Bing Places helps businesses appear in map and local packs similar to Google My Business.
Reviews are pulled from sources like Yelp and Facebook.
Shopping Search shows product listings, prices, and comparisons. Using structured product markup helps pages appear in these results.
Visual Search allows users to upload or capture an image to search visually related content.
Web Search APIs allow developers to build custom search functions using Bing’s engine.
Edge and Windows integration keeps Bing close to users. It’s built into Microsoft’s browser and search bar, ensuring high visibility.
These verticals connect directly to Bing’s main index. The same ranking logic applies but adapted for each content type.
Final Thoughts & Action Steps
At its core, Bing is not wildly alien – it operates on the same founding principles as other search engines: crawl, index, rank. But its priorities, weightings, and integrations differ enough that treating it like a “Google clone” can leave performance on the table.
If you want to dominate in Bing, here’s your checklist:
- Validate & submit site in Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Enable IndexNow, submit your sitemap, and maintain high content freshness.
- Audit your pages for crawlability: avoid JavaScript-only content, fix broken links, and maintain a clean structure.
- Optimize on-page elements literally – exact keyword matches in title, URL, H1, meta tags.
- Use Schema.org markup to earn rich results.
- Strengthen backlink profile, focusing also on authoritative sources.
- Encourage social sharing & engagement – they matter more on Bing.
- Monitor performance in Bing-specific tools, detect drop-offs, and troubleshoot.
- Experiment with vertical content types – images, video, shopping to find opportunities.
- Don’t forget about AI features – Make sure your content is set up so that Bing’s summarization and AI generative layers can read it easily.
If you do these things, you won’t just “work for Bing,” you’ll make Bing work for you.
Final Thoughts
Bing is not just a smaller version of Google. It has its own way of thinking, its own likes and dislikes, and its own strengths. It prioritizes structure, clarity, novelty, and meaningful user engagement.
As AI changes the way we search, Bing’s core value stays the same: discover the most useful, reliable stuff and provide it to users in a way that helps them make decisions faster.
You can get Bing to work for you if you know how it works.
Have more questions on how the Bing search engine works or need help managing search results on Bing? Contact NewReputation today.